
Regular exfoliation is one of the most important steps in attaining healthy, glowing skin. Exfoliation is a process in which dead skin cells are removed, preventing pores from getting clogged and revealing a smooth layer of skin. The process of exfoliation can be either physical or chemical. While physical exfoliation is typically achieved using a textured facial scrub, chemical exfoliation uses chemical products to break down and remove dead skin.
If you’re pursuing a career as an esthetician, you’ll be trained in performing chemical exfoliation treatments, helping clients with different skin types to safely brighten their skin and manage breakouts. Below, discover more about what a chemical exfoliation procedure entails, as well as some tips for successfully administering them to clients throughout your career.
How Does a Chemical Exfoliation Work?
Chemical exfoliation - sometimes referred to as a light chemical peel - is a procedure in which a chemical agent is applied to reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, pigmentation and pores or acne. The most frequently used chemical exfoliators are those which contain beta hydroxy acids (BHAs) or alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs). After earning your medical esthetician diploma, you’ll likely use a few different types of chemicals in this process, including enzymes, retinoids, peptides and acids such as glycolic acid, salicylic acid, lactic acid, trichloroacetic acid and carbolic acid. When these acids are applied, the bond by which dead skin cells attach to the face is broken down. This allows these ingredients to penetrate deeper into the skin, resulting in a much smoother, glowing appearance for clients once the procedure is complete.
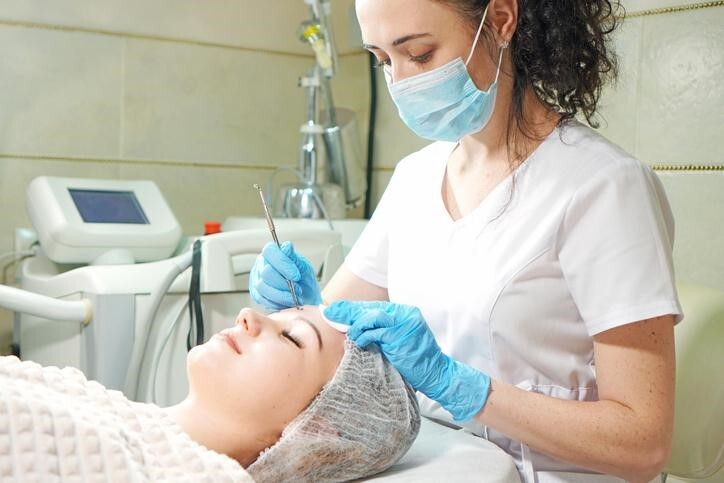
After earning your medical esthetician diploma, you’ll possess the skills to perform chemical exfoliations
Customizing the Chemical Exfoliation Process for Your Client
As a graduate of a medical esthetician program, you can use your understanding of the various enzymes and acids to create a customized experience for your clients. When it comes to chemical exfoliation, customization is important, as different skin types are prone to different reactions when they come into contact with chemicals.
When clients arrive for a chemical exfoliation, ask them about their goals for their skin, their reasons for considering a chemical exfoliation and whether they have any allergies or sensitivities. This information will allow you to determine the right kinds of products to use. For example, clients with acne-prone skin will be better off with a BHA, while those seeking to reduce wrinkles might benefit from the use of an AHA or a retinoid.
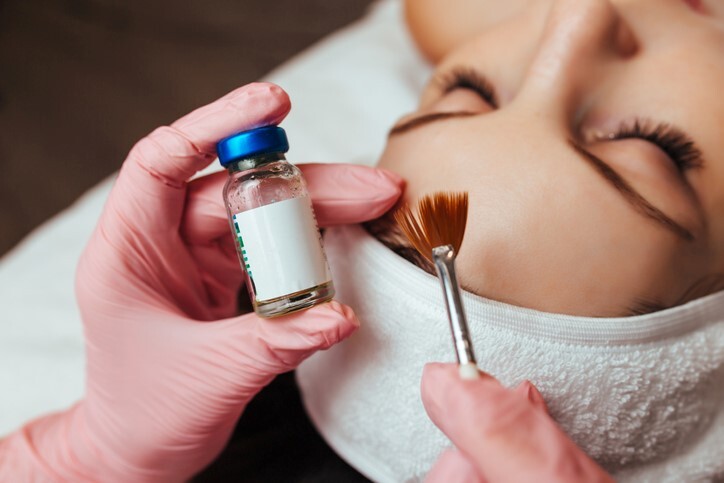
As an esthetician, you can customize the chemical exfoliation procedure to the client
Precautions to Take After Earning Your Medical Esthetician Diploma
Because the chemical exfoliation process requires extensive knowledge of the ingredients being used for the safety of the client’s skin, it’s important that only trained professionals perform them. Once you’ve completed your training, you can take a few precautionary steps to ensure that your client's skin is not damaged by the chemical exfoliation procedure.
For one, you’ll want to make sure that the client’s face is thoroughly cleansed and dry before applying the exfoliator. Once the exfoliator is applied and dried, a hydrating moisturizer should be applied every few hours. Chemical exfoliants can make the skin prone to dryness, and recommending an appropriate moisturizer to your clients can help them to prevent this from occurring. Lastly, normal skincare products should only be used once the skin has recovered from the aftereffects of the procedure, which might take up to a few days. When you keep these precautionary measures in mind, you’ll be able to successfully administer chemical exfoliation during your career as an esthetician.
Are you interested in enrolling in a medical esthetician course?
Start training for a career with a program at Algonquin Careers Academy today!


